Plastic recycling
Over 6.15 million tonnes of plastic waste must be properly processed each year in Germany to prevent environmental damage and protect valuable raw material resources. We support plastic recyclers with high-performance products and tailored solutions that help them operate their recycling plants as efficiently as possible.
Discover Our Spare and Wear Parts
Discover Our Spare and Wear Parts
80% ↓
80% of plastic packaging recycling takes place in Germany.
20% ↓
Nearly 20% of plastic packaging recycling takes place across the rest of Europe.
99,4% ↓
Of the 5.7 million tonnes of plastic waste generated in Germany in 2021, 99.4% was recovered. 64% through energy recovery, 34% via mechanical recycling, and 0.4% through chemical recycling.
Efficient Solutions for Plastic Recycling
With over 25 years of experience, CUTMETALL delivers effective solutions for challenges in plastic recycling. Our focus lies on durable spare and wear parts that optimise processes and reduce costs.1. Corrosion-resistant machine components
CUTMETALL’s repair kits enable quick fixes using weldable plates – no extensive machine modifications required.2. Optimised solutions for reversing machines
Our innovative knife holders provide effective protection for screws, significantly extending service life.3. Efficient shredding of abrasive plastics
The Carbide range features tungsten carbide blades with single or multi-part brazed edges for tough, abrasive materials.4. Personalised consulting and problem-solving
CUTMETALL supports customers not only with premium products, but also with on-site consulting. Our experts analyse operational processes and develop tailored optimisation strategies – even for recurring machine issues.With CUTMETALL, you increase the efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness of your plastic recycling systems!
Register in our shop

An insight into plastics recycling



Further
Processing of Materials
Depending on the type, plastics can be melted down or chemically broken apart for further processing.
In some cases, they can also be used for energy recovery through incineration.
Ready to optimise your plastic recycling process? Let’s get going!
Curious about how plastic recycling works and its environmental benefits?
Learn about the process and key advantages. Scroll down
Learn about the process and key advantages. Scroll down
What Does Plastic Recycling Mean?
Plastic recycling is becoming increasingly important – not only in the context of climate change, but also for environmental protection. However, recyclers face several challenges during the recovery process:- Severe wear on machine parts: Different types of plastic waste and residual moisture cause excessive wear, which shortens machine service life.
- High costs due to machine downtime: Frequent equipment shutdowns for replacing shredder knives and screens lead to high energy costs and extended downtimes, slowing overall production.
- Adapting to varying materials: To operate efficiently, recyclers must have machine parts that are tailored to specific types of plastic waste.

Minimized downtime
Minimized downtime thanks to fewer knife changes in the machinesMinimized downtime thanks to fewer knife changes in the machines
Development of customized
solutions
solutions
With over 25 years of experience, our experts develop extremely wear-resistant, customized solutions specifically for the field of plastics recycling.
Cost Reduction
Reduced machine vibrations, lower energy consumption, and longer maintenance intervals reduce your costs.
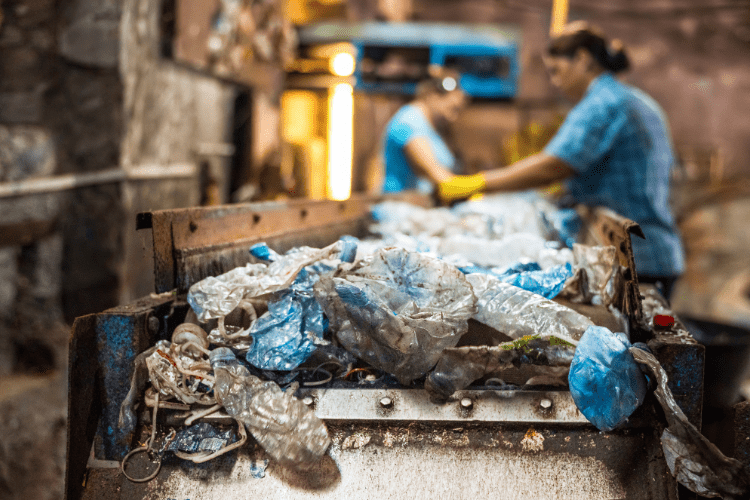

How Does Plastic Recycling Work?
Plastic recycling involves processing used plastic waste—usually collected in yellow bins—into new products. The process begins with sorting and cleaning the plastics. After that, the material is shredded—a step where our area of expertise, industrial shredding, comes into play. Depending on the type of plastic, it is either granulated, chemically broken down into base components, or used for energy recovery through incineration. The ultimate goal is to reduce waste, protect the environment, and conserve valuable resources.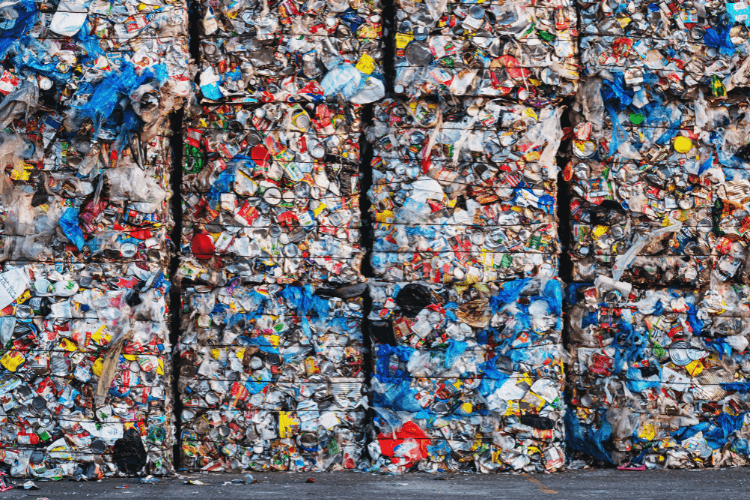
What Are the Challenges in Plastic Recycling?
Material Inhomogeneity:
Plastic waste often contains a mix of soft and hard plastics along with disruptive contaminants. This variation complicates processing and demands flexible workflows and durable equipment.Contaminants:
Even pre-sorted plastic waste may contain unexpected impurities that increase wear on knives and machinery.Quality Loss:
Recycled plastics are often of lower quality than virgin materials. Removing contaminants and adjusting machinery is essential to meet quality standards.Machine Downtime:
To ensure output quality, machines must be stopped regularly for refitting with suitable knives and screens. Every stoppage costs both time and money.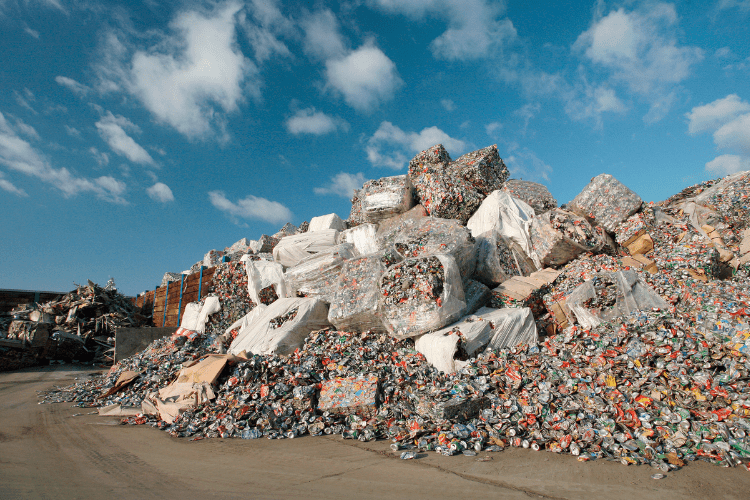
Why Is Plastic Recycling Becoming More and More Important?
Plastic waste recycling is becoming increasingly important – for three key reasons:
To address these challenges, the European Commission introduced a Plastic Waste Strategy in 2018 to reform the way plastics are managed. A core element is increasing the share of mechanical recycling of plastic waste from households. Certain plastics like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are recyclable and serve as valuable raw materials for producing new products.
Mechanical Recycling
33% of plastic waste in Germany is mechanically recycled. This involves shredding, cleaning, and sorting the plastic, which is then melted at high temperatures and reprocessed. Only thermoplastics—plastics that become pliable when heated—are suitable for this method.
Energy Recovery
At 44%, this method makes up the largest share. Contaminated or mixed plastics are incinerated, and the heat generated is used for energy.
Chemical Recycling
Just 1% of plastic waste is chemically recycled. This process breaks down polymers into monomers, oils, and gases using chemical reactions, which can then be used to produce new plastics. The EU’s strategy aims to make plastic recycling more profitable by improving recyclability requirements, boosting demand for recycled materials (recyclates), expanding infrastructure, and standardising waste collection and sorting across the EU.
- Rapid increase in packaging waste: In recent years, the amount of packaging discarded has grown significantly, leading to more plastic waste that must be recycled.
- More microplastics in the oceans: Plastics break down in water into tiny particles called microplastics, which pollute the seas and harm wildlife and ecosystems. Proper recycling helps prevent this.
- China’s ban on plastic waste imports: China has severely restricted imports of plastic waste, forcing former exporters to develop their own recycling solutions.
To address these challenges, the European Commission introduced a Plastic Waste Strategy in 2018 to reform the way plastics are managed. A core element is increasing the share of mechanical recycling of plastic waste from households. Certain plastics like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) are recyclable and serve as valuable raw materials for producing new products.
Mechanical Recycling
33% of plastic waste in Germany is mechanically recycled. This involves shredding, cleaning, and sorting the plastic, which is then melted at high temperatures and reprocessed. Only thermoplastics—plastics that become pliable when heated—are suitable for this method.
Energy Recovery
At 44%, this method makes up the largest share. Contaminated or mixed plastics are incinerated, and the heat generated is used for energy.
Chemical Recycling
Just 1% of plastic waste is chemically recycled. This process breaks down polymers into monomers, oils, and gases using chemical reactions, which can then be used to produce new plastics. The EU’s strategy aims to make plastic recycling more profitable by improving recyclability requirements, boosting demand for recycled materials (recyclates), expanding infrastructure, and standardising waste collection and sorting across the EU.
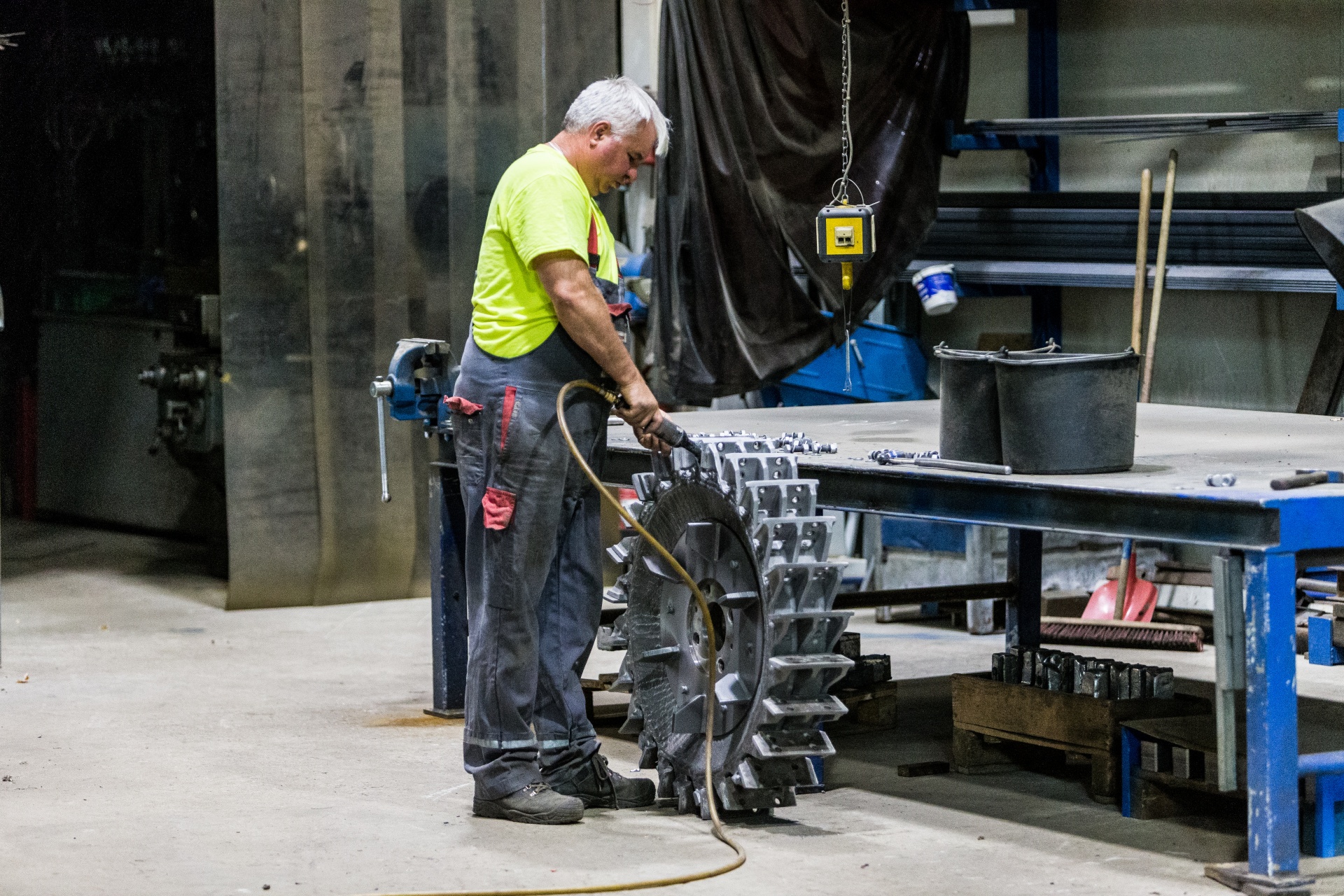

Typical Challenges in Plastic Recycling
- Moisture in plastic waste: Residual liquids in bottles and containers can trigger chemical reactions that cause machine parts to rust.
- High wear and tear: Frequent changes in cutting direction cause faster wear of mounting screws, making blade replacement more difficult.
- Use of various knives and screens: Different types of machine knives and screens are required to handle diverse materials. For example, unsuitable knives may cut stretch film into larger pieces, making further processing harder.
- Economic factors: High wear and the need for optimal machine configuration make it essential to minimise downtime. The right knives and screens save time, reduce costs, and limit wear.
What Makes Our Plastic Recycling Products So Special?
The base material of our extremely wear-resistant carbide blades is a specially treated tool steel.
The inlays are brazed with hard solder, keeping the core structure flexible while ensuring that the blade body can withstand heavy loads.
CUTMETALL also finishes its machine blades using diamond grinding technology, which ensures long-lasting sharpness even under high stress.
Equipped with highly wear-resistant rotor and stator blades (crown cutters, block, granulating and flat knives), as well as particularly durable screens, the machines deliver a consistently uniform cut output over long operating periods. At the same time, fewer required blade changes reduce machine downtime.
The result is higher production throughput, improved output quality and stable bulk densities.
Even the machines themselves benefit from CUTMETALL products: they reduce vibrations, lower noise emissions, decrease energy consumption, reduce heat build-up, minimise dust, and extend maintenance intervals.
Equipped with highly wear-resistant rotor and stator blades (crown cutters, block, granulating and flat knives), as well as particularly durable screens, the machines deliver a consistently uniform cut output over long operating periods. At the same time, fewer required blade changes reduce machine downtime.
The result is higher production throughput, improved output quality and stable bulk densities.
Even the machines themselves benefit from CUTMETALL products: they reduce vibrations, lower noise emissions, decrease energy consumption, reduce heat build-up, minimise dust, and extend maintenance intervals.