Tyre Recycling
Every year, around 3.4 million tonnes of used tyres are generated in Europe. As they do not decompose naturally, worn-out tyres must be professionally disposed of. CUTMETALL products help tyre recycling facilities optimise their machinery and produce high-quality rubber granulate and powder.
View our products
View our products
3.4M ↓
Each year, around 3.4 million tonnes of used tyres are generated in Europe alone.
20% ↓
In Germany, 20% of used tyres are given a second life as part-worn tyres or casings.
+40% ↓
More than 40% are processed into granules and rubber powder in Germany. These materials are used in construction and noise protection products, load securing systems, railway track installations, and the cement industry.
Efficient Solutions for Tyre Recycling with CUTMETALL
Tyre recycling places high demands on machinery and wear parts. At CUTMETALL, we offer robust and durable components specifically engineered for these challenging processes.
Our enhanced wear parts for recycling machinery are designed for exceptional resistance. For you, this means:
- Longer service life for machine components
- Higher throughput and optimised system performance
- Consistent output material thanks to precision screens and perforations
- Minimised downtime due to high stock availability
We supply replacement and wear parts for many renowned tyre shredder brands including MeWA Recycling, Eldan Recycling, Artech, Adelmann, BHS, THM Recycling and Herbold.
Register in our shop
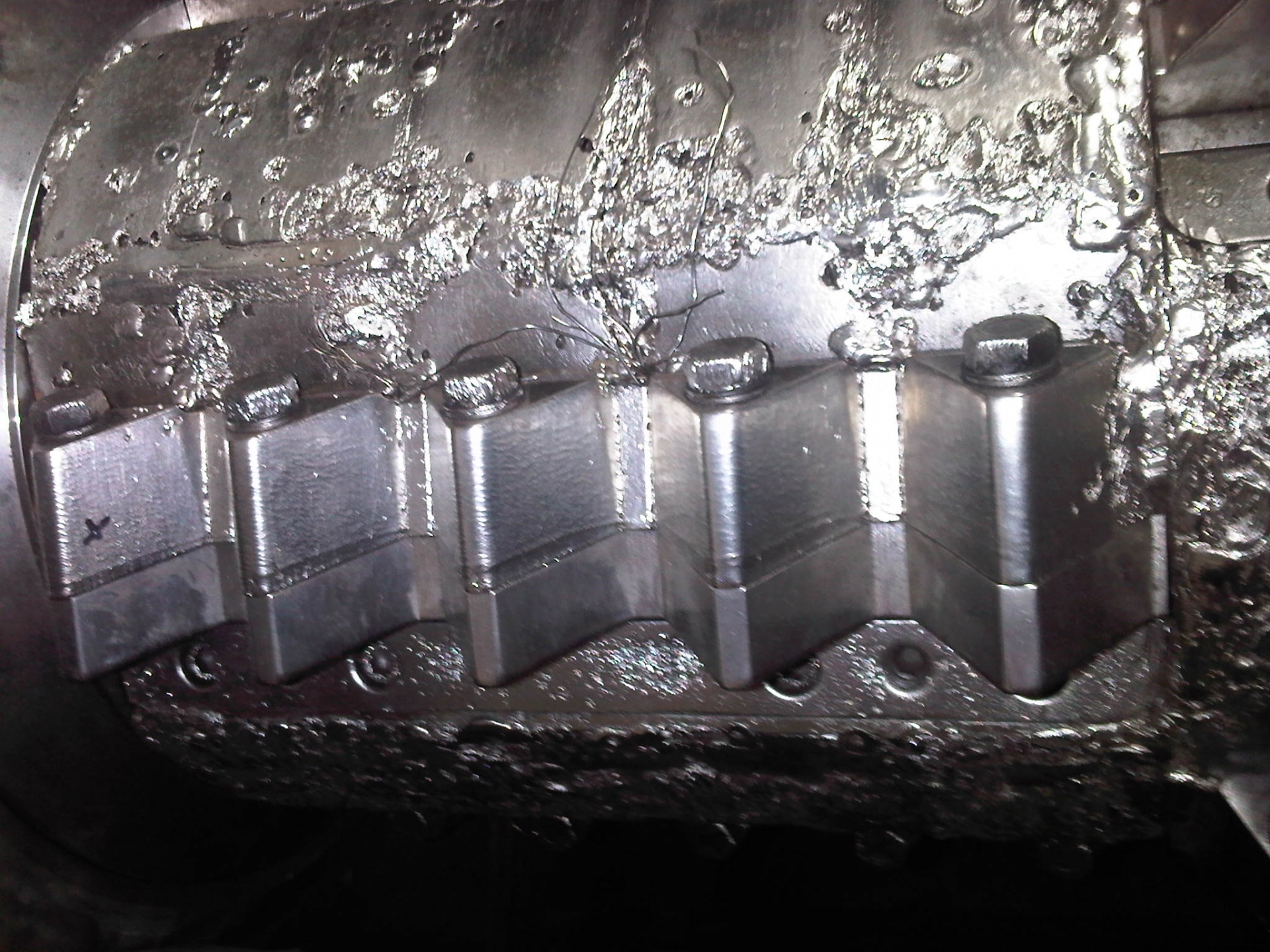

An overview of used tyre recycling
.png)
.png)
.png)
Ready for the next step? Let’s get started!
Interested in more details about tyre recycling? Discover the process and its advantages now.
Continue reading
Continue reading

What Is the Impact of Tyre Recycling?
Recycling used tyres plays a key role in environmental protection and in conserving valuable resources. In Germany, the Circular Economy Act ensures that old and worn car tyres are not simply thrown away but are properly disposed of and recycled.There are several ways in which used tyres can be recovered: They can be retreaded by applying a new rubber layer to the existing carcass, broken down into raw materials for reuse, or thermally processed to recover energy — known as energy recovery or thermal recycling.
What are the challenges in tyre recycling?
The challenges of tyre recycling are primarily due to the complex composition of tyres:
Only regular replacement of wear parts ensures high performance levels in the recycling facility — enabling production of high-quality rubber output and positioning recyclers as reliable suppliers.
- Toxic components: Modern tyres contain carbon black with toxic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), complicating recycling and posing environmental risks.
- High steel content: A tyre is made up of around 18% steel, embedded in the bead as wire. This steel must be separated before shredding.
- Severe wear: The hard steel causes significant machine wear during shredding. Recycling equipment is subject to high stress and requires frequent replacement of wear parts.
Only regular replacement of wear parts ensures high performance levels in the recycling facility — enabling production of high-quality rubber output and positioning recyclers as reliable suppliers.


What are the environmental impacts of producing tyres from recycled materials compared to new ones?
Manufacturing tyres from recycled materials offers significant environmental benefits compared to using virgin raw materials:
Reduced Use of Fossil Resources:
Using recycled materials such as PET bottles or end-of-life tyres lowers the demand for new fossil-based resources. Manufacturers like Continental already use up to 28% sustainable materials from bio-based or circular sources.Lower Energy Consumption:
Producing polyester yarn from recycled PET uses significantly less energy than manufacturing it from virgin resources – conserving energy and reducing the environmental impact.Less Waste:
Recycling PET bottles – around 9 to 15 per tyre – and other materials helps prevent this waste from ending up in landfills or incineration plants.Reducing CO₂ Emissions:
Using recycled raw materials helps lower CO₂ emissions in tyre manufacturing, reducing the overall environmental footprint.Protecting Natural Resources:
In addition to recycled plastics, residual materials from the paper and timber industries as well as rice husks are also used – helping preserve valuable natural resources.Promoting the Circular Economy:
Integrating recycled materials into production supports the development of a functioning circular economy, where raw materials remain in use for as long as possible.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to note that the environmental impact can vary depending on the recycling process and the materials used.
Moreover, tyre quality must be high to ensure durability and fully realise the environmental benefits.

Regulatory Framework for Tyre Recycling – Example: Germany
Tyre recycling in Germany is governed by clear legal requirements under the Circular Economy Act and specific waste tyre regulations. A key element is the landfill ban, which promotes sustainable recovery methods and increases recycling rates.Manufacturers and importers are required to collect and properly recycle waste tyres, contributing to market stability. At the same time, government support programmes drive the development of innovative recycling technologies.
Legally defined quality standards ensure demand for high-grade recycled products and encourage their use across various industries, promoting a sustainable circular economy.
Differences in Tyre Recycling between Germany and the USA
How does the regulatory framework differ?
In Germany, tyre recycling is strictly regulated by the Circular Economy Act and the Waste Tyre Ordinance. A landfill ban ensures that used tyres are not sent to landfill sites. In the USA, regulations vary by state, as there is no nationwide landfill ban.
Who is responsible for tyre recycling?
In Germany, manufacturers and importers are legally obliged to organise the collection and recycling of used tyres. In the USA, responsibility often lies with individual states or local authorities, leading to differing regulations.
What are the recycling rates?
Germany achieves a recovery rate of around 90%, thanks to strict legislation and well-established systems. In the USA, recycling rates vary widely between states.
Which recovery methods are used?
Germany relies on material recovery and energy utilisation, for example in the cement industry. In the USA, more tyres are landfilled, but there are also innovative applications such as use in asphalt mixtures.
How is the tyre recycling market structured?
The German market is centralised, with a few major players. In the USA, the system is more decentralised, with many regional recycling firms.
Are there differences in research and development?
Germany invests heavily in new recycling technologies and innovative applications, supported by public funding. In the USA, research activities also exist, but are less nationally coordinated.
What about public awareness?
Environmental awareness is high in Germany, and recycling is deeply embedded in society. In the USA, awareness is growing but varies by region.
Conclusion: Germany has a strict and uniform system, while the USA shows potential for improvement through national coordination and innovative recycling methods.
In Germany, tyre recycling is strictly regulated by the Circular Economy Act and the Waste Tyre Ordinance. A landfill ban ensures that used tyres are not sent to landfill sites. In the USA, regulations vary by state, as there is no nationwide landfill ban.
Who is responsible for tyre recycling?
In Germany, manufacturers and importers are legally obliged to organise the collection and recycling of used tyres. In the USA, responsibility often lies with individual states or local authorities, leading to differing regulations.
What are the recycling rates?
Germany achieves a recovery rate of around 90%, thanks to strict legislation and well-established systems. In the USA, recycling rates vary widely between states.
Which recovery methods are used?
Germany relies on material recovery and energy utilisation, for example in the cement industry. In the USA, more tyres are landfilled, but there are also innovative applications such as use in asphalt mixtures.
How is the tyre recycling market structured?
The German market is centralised, with a few major players. In the USA, the system is more decentralised, with many regional recycling firms.
Are there differences in research and development?
Germany invests heavily in new recycling technologies and innovative applications, supported by public funding. In the USA, research activities also exist, but are less nationally coordinated.
What about public awareness?
Environmental awareness is high in Germany, and recycling is deeply embedded in society. In the USA, awareness is growing but varies by region.
Conclusion: Germany has a strict and uniform system, while the USA shows potential for improvement through national coordination and innovative recycling methods.