Plastic recycling
More than 6.15 million tons of plastic waste must be properly treated in Germany every year to avoid environmental harm and conserve essential raw material resources.
We support plastic recycling companies with powerful products and customised solutions that enable highly cost-effective plant operation.
Explore Our Spare and Wear Parts
Explore Our Spare and Wear Parts
80% ↓
80% of plastic packaging recycling happens in Germany.
20% ↓
Close to 20% of plastic packaging recycling occurs throughout the rest of Europe.
99,4% ↓
Of the 5.7 million tons of plastic waste produced in Germany in 2021, 99.4% was recovered. 64% through energy recovery, 34% through mechanical recycling, and 0.4% through chemical processing.
Effective Solutions for Plastic Recycling
With over 25 years of experience, CUTMETALL provides powerful solutions to the challenges of plastic recycling. We focus on long-lasting spare and wear parts that streamline operations and reduce costs.1. Stainless machine components
CUTMETALL’s repair kits allow for fast maintenance using weld-in plates – no major machine conversions needed.2. Optimized systems for reversing machinery
Our innovative knife holders effectively shield screws from wear, extending component life.3. Efficient shredding of abrasive plastics
The Carbide series offers tungsten carbide blades with single or multi-part brazed cutting edges for highly abrasive materials.4. Tailored advice and problem-solving
CUTMETALL provides more than high-quality products – we also deliver personal support. Experts visit your site to analyse workflows and develop custom solutions, including for persistent equipment issues.With CUTMETALL, you enhance the efficiency, durability, and profitability of your plastic recycling operations!
Sign up for the store

An insight into plastics recycling



Material
Processing and Refinement
Plastics can be melted or chemically broken down, depending on their type, and then reprocessed.
In some cases, they can also be used as an energy source through combustion.
Ready to improve your plastic recycling process? Let’s get started!
Curious about how plastic recycling works and its environmental impact?
Keep reading to discover the full process and key benefits. Scroll down
Keep reading to discover the full process and key benefits. Scroll down
What Does Plastic Recycling Involve?
Plastic recycling is becoming more important than ever—not just to combat climate change, but also to protect the environment. Still, recyclers face several challenges during the reuse process:- Heavy wear on machine components: Mixed plastic materials and residual moisture accelerate wear and tear, shortening equipment lifespan.
- High operational costs from equipment downtime: Frequent shutdowns for changing shredder blades and screens increase energy consumption and production delays.
- Need for material-specific equipment: To maintain efficiency, recyclers must keep the right machine parts on hand for each type of plastic waste.

Minimized downtime
Minimized downtime due to reduced blade changes in the machines
Development of customized
solutions
solutions
With over 25 years of experience, our experts develop extremely wear-resistant, customized solutions specifically for plastics recycling applications.
Cost reduction
Reduced machine vibrations, reduced energy consumption and extended maintenance intervals reduce your costs.
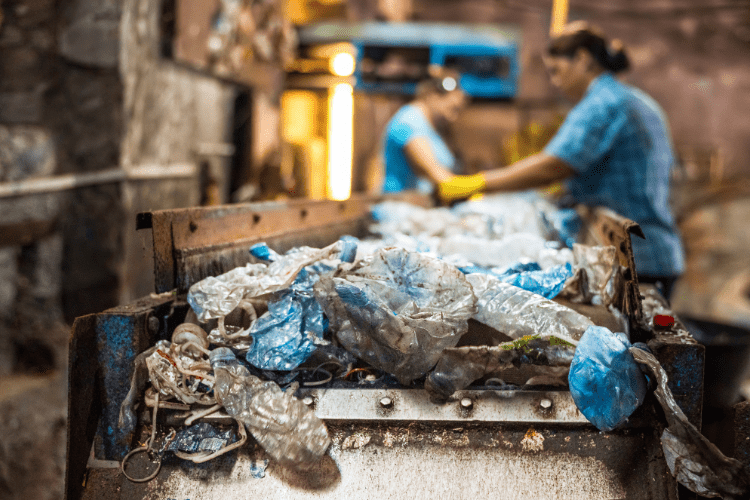

How Does Plastic Recycling Work?
Plastic recycling starts with processing used plastic waste—typically collected in yellow bins—to create new products. The process begins with sorting and cleaning the materials. Then, the waste is shredded—this is where our expertise in industrial shredding comes in. Depending on the type of plastic, the material is either turned into granules, broken down into its chemical building blocks, or incinerated for energy recovery. The main goal is to reduce waste, protect the environment, and conserve valuable raw materials.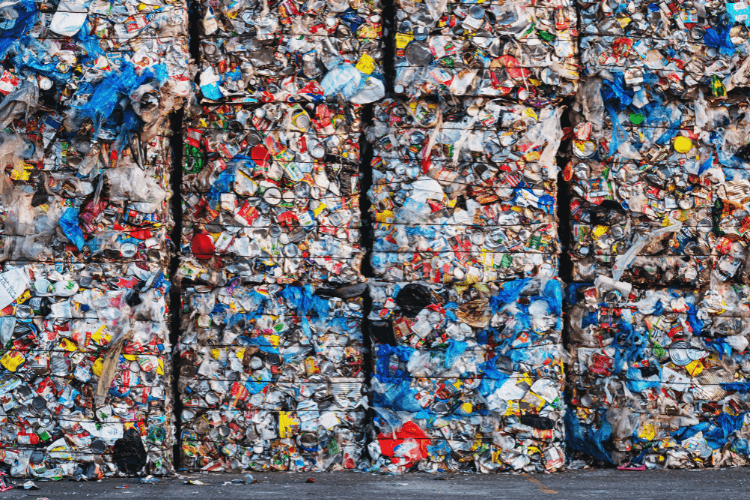
What Are the Main Challenges in Plastic Recycling?
Material Inconsistency:
Plastic waste often includes a blend of soft and rigid plastics, as well as foreign materials. This complexity requires adaptable processing systems and heavy-duty machines.Contamination:
Pre-sorted plastic waste frequently contains unexpected contaminants that can accelerate the wear of machinery and blades.Quality Reduction:
Recycled plastics are typically lower in quality than virgin material. To achieve the desired output quality, contaminants must be removed and machines must be properly adjusted.Equipment Downtime:
Maintaining material quality requires machines to be stopped regularly for blade and screen changes. Each shutdown results in time loss and additional cost.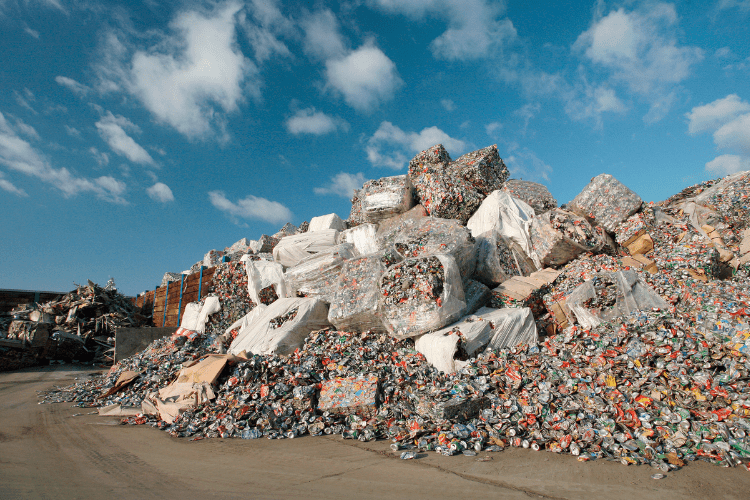
Why Is Plastic Recycling Growing in Importance?
Plastic recycling is growing in importance for three main reasons:
To tackle these issues, the European Commission introduced a Plastic Waste Strategy in 2018, setting new standards for plastic management. A key focus is to increase the share of mechanical recycling of household plastic waste. Plastics like PET (polyethylene terephthalate) can be recycled and reused as valuable raw materials for new products.
Mechanical Recycling
33% of Germany’s plastic waste is mechanically processed. This includes shredding, cleaning, and sorting the plastic, then melting and reprocessing it. Only thermoplastics are suitable for this method.
Energy Recovery
Accounting for 44%, energy recovery is the most common method. Plastic waste is burned to generate energy, especially in the case of contaminated or mixed materials.
Chemical Recycling
Just 1% of plastic waste is chemically recycled. In this method, chemical reactions break down long polymer chains into monomers, oils, and gases that can be used to produce new plastic. Through this strategy, the EU seeks to make plastic recycling economically viable by enforcing new packaging rules, boosting recyclate demand, expanding recycling capacity, and implementing a standardised EU-wide collection and sorting system.
- Surge in packaging waste: In recent years, the volume of discarded packaging has increased dramatically, creating more plastic waste that needs to be recycled.
- Rise in ocean microplastics: Plastic breaks down in water into tiny fragments known as microplastics, which pollute oceans and harm marine life and ecosystems. Recycling plays a key role in prevention.
- China’s plastic waste import ban: With China restricting plastic waste imports, countries that once exported their plastics must now manage recycling domestically.
To tackle these issues, the European Commission introduced a Plastic Waste Strategy in 2018, setting new standards for plastic management. A key focus is to increase the share of mechanical recycling of household plastic waste. Plastics like PET (polyethylene terephthalate) can be recycled and reused as valuable raw materials for new products.
Mechanical Recycling
33% of Germany’s plastic waste is mechanically processed. This includes shredding, cleaning, and sorting the plastic, then melting and reprocessing it. Only thermoplastics are suitable for this method.
Energy Recovery
Accounting for 44%, energy recovery is the most common method. Plastic waste is burned to generate energy, especially in the case of contaminated or mixed materials.
Chemical Recycling
Just 1% of plastic waste is chemically recycled. In this method, chemical reactions break down long polymer chains into monomers, oils, and gases that can be used to produce new plastic. Through this strategy, the EU seeks to make plastic recycling economically viable by enforcing new packaging rules, boosting recyclate demand, expanding recycling capacity, and implementing a standardised EU-wide collection and sorting system.
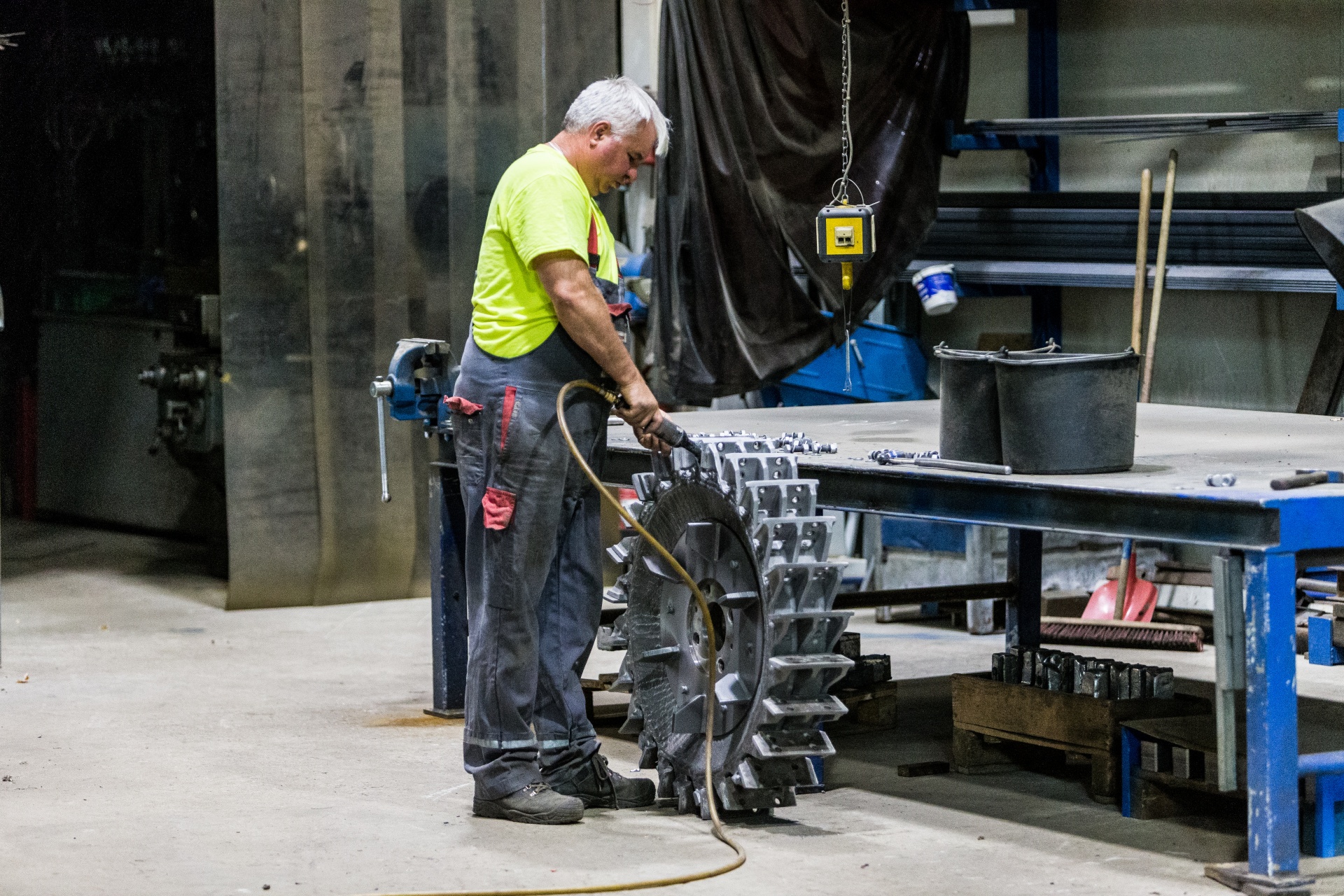

Common Issues in Plastic Recycling
- Moisture in plastic waste: Leftover liquids in bottles and containers can lead to chemical reactions that cause machine components to rust.
- Excessive wear: Frequent changes in blade direction accelerate the wear on fastening screws, making blade changes more difficult.
- Need for specific blades and screens: Different blades and screens are needed for various types of materials. For example, using the wrong blades to cut stretch film may result in larger pieces that complicate further processing.
- Economic considerations: High wear rates and the need for properly equipped machines make it crucial to minimize downtime. The right blades and screens help save time, reduce expenses, and minimize wear.
What Makes Our Plastic Recycling Products Stand Out?
The core material of our ultra wear-resistant carbide blades is a specially hardened tool steel.
The inlays are hard-brazed, allowing the base structure to remain flexible while the blade body resists heavy mechanical stress.
CUTMETALL also uses diamond grinding to finish its blades, delivering excellent edge retention even under intensive workloads.
With highly durable rotor and stator knives (crown cutters, block, granulator, and flat blades) and extra wear-resistant screens, machines produce consistent and homogeneous output over extended periods. Fewer blade changes also mean reduced downtime.
The result: increased production uptime, higher output quality, and consistent bulk density.
And the machines themselves benefit from CUTMETALL products: they reduce machine vibration, lower operating noise, cut energy usage, limit temperature rise, reduce dust exposure, and extend service intervals.
With highly durable rotor and stator knives (crown cutters, block, granulator, and flat blades) and extra wear-resistant screens, machines produce consistent and homogeneous output over extended periods. Fewer blade changes also mean reduced downtime.
The result: increased production uptime, higher output quality, and consistent bulk density.
And the machines themselves benefit from CUTMETALL products: they reduce machine vibration, lower operating noise, cut energy usage, limit temperature rise, reduce dust exposure, and extend service intervals.